Battery Maintenance
Learn How To Safely Keep Your Batteries in Their Best Shape
Battery Inventory Management
Storage
- How do I store batteries before they’re sold? Batteries should always be stored upright and be easy to access. Batteries should always be protected from shorts and never have tools or other materials stored on top of or near the battery terminals.
- Do environmental factors matter for battery storage? For optimal performance, batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place. Batteries stored in especially cold or warm environments need to be examined and maintained more frequently. Electrolyte levels, indicators of sulfation, and state of charge should all be monitored.
- Storing batteries in an organized fashion with like types stored together is a best practice.
- Batteries should NEVER be piled one on top of the other.
Stock Rotation
- Why is stock rotation important? First in first out (FIFO) inventory management should be applied, as batteries have a shelf life. Quality batteries can be stored for longer periods of time with proper maintenance. Proper stock rotation allows you to keep your battery inventory as fresh as possible.
- How do I implement stock rotation practices? Keep detailed records of shipments and adhere to the FIFO rule. These practices will also help you know when it’s time to order more batteries.
Battery Maintenance
- Why do batteries need to be maintained on-shelf? All batteries self-discharge at a rate differing by battery chemistry. Periodic maintenance charging and cleaning will help offset self-discharge and provide the best customer experience for when the battery is installed in an application.
Battery Stock Maintenance
A responsible service person should be given the responsibility of the designated battery storage area and the maintenance of stored batteries. Maintenance duties and the appropriate safety procedures should be clearly explained. Proper tools and equipment are necessary. Training on these tools is imperative.
Equipment should include an appropriate battery charger, hydrometer, and a thermometer. A carrying strap, terminal cleaner, water filler, and a supply of baking soda for the neutralization of acid should also be available.
The battery room, or storage area, should be equipped with adequate ventilation. Safety equipment such as eye protection, rubber gloves, safety shoes, acid proof clothing, etc., are necessary as well. Eye wash devices should also be available in case of emergencies. It is also recommended to assemble an acid spill kit in case of accidental battery damage and subsequent spillage of battery electrolyte.
Consult your local and state laws for any applicable regulations that must be met.
Continental Battery Systems sells the majority of the items needed for proper maintenance. Contact your rep for additional information and pricing!
Self-Discharge
All batteries will slowly lose charge when not in service. This occurrence is known as self-discharge.
The rate of self-discharge increases in higher ambient temperature environments; this is true for maintenance, maintenance free, and deep cycle batteries. Other battery chemistries such as AGM, GEL, and Lithium Iron Phosphate self-discharge at differing rates than flooded lead acid batteries, but are still affected by extreme temperatures and also require proper maintenance.
Allowing batteries to be stored for an extended period of time without recharging, will result in reduced performance and service life. To preserve optimum battery performance and life, recharge stored flooded lead acid battery types when the open circuit voltage drops to 12.4 volts.
Consult the appropriate battery manufacturer's instruction manual for details regarding manufacturer specific best practices. The chart below is an approximated state of charge graph for flooded lead acid batteries based on open circuit voltage.
Instructions For Charging a Battery
The room or compartment where the battery is being charged should be well-ventilated. Do not put a battery on the charger unless you wear safety goggles and a face shield. It must be assumed that explosive mixtures of hydrogen gas are always present within the battery cells. Even a battery standing idle generates small quantities of hydrogen due to the self-discharge action. This gas collects in the cells and can be exploded by a torch, match flame, lighted cigarette, sparks from loose connections, or metal tools making contact between the terminals, the ungrounded terminal, and adjacent metal grounded parts.
Since vent cap designs having flame barrier features are not easily distinguished from other style vent caps, it is recommended that vent caps be left on the battery during charging. As a precaution, place a wet cloth over the battery and vent caps. Since flame arresters are used in most modern vent cap designs to reduce the possibility of the battery being exploded by an external spark, this safety feature could be bypassed by removing the vent caps. Whether such vent caps are present or not, always shield your eyes when working around the battery and follow the precautions covered here.
Do not charge a battery unless you are familiar with the step-by-step procedure. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the charger. If the instructions are no longer legible and you do not have literature containing the instructions, then obtain the instructions from the charger manufacturer. Never use a charger without instructions. Turn the charge rate switch and timer to the “OFF” position before connecting the leads to the battery. Next, connect the charger leads to the battery terminals. Red positive (+) lead to the positive terminal, and black negative (-) lead to the negative terminal. If the battery is in the car, connect the negative lead to the engine block if the car has a negative ground (negative battery terminal is connected to ground). Connect the positive lead to the ground if the car has a “positive ground” (now rarely occurs). “Rock” the charger lead clamps to make certain a good connection has been made. Set the electric timer to the desired charging time. Now, turn on the charger and slowly increase the charging rate until the desired ampere value is reached. Do not charge in the red zone. If smoke or dense vapor comes from the battery, shut off the charger and reject the battery. If violent gassing or spewing of electrolytes occurs, reduce or temporarily halt the charging.
Never touch the charger leads when the charger is “ON.” This could break a connection at the battery terminal, creating a spark that could ignite the explosive gases in the battery. Never break a “live” circuit at the battery terminals for the same reason. Always turn the charger “off’ before removing a charger lead from the battery.
When charging or testing a side terminal battery out of a vehicle, always use side terminal charging and testing posts designed for this purpose.
Special Charging Instructions for AGM and Gel Batteries
Constant-Voltage Method (Recommended Method)
AGM and gel batteries are sensitive to high-voltage charging (above 14.4 volts). The recommendation is to use a 6- to 12-amp, 12-volt automatic charger set at the regular setting. If you use a non-automatic charger, you need to monitor the voltage so it does not exceed 14.4 volts and/or 12 amps at any time during recharge. This battery needs recharging only if the open-circuit voltage (O.C.V.) is below 12.5 volts. DO NOT OVERCHARGE.
Battery Recharging Time Chart
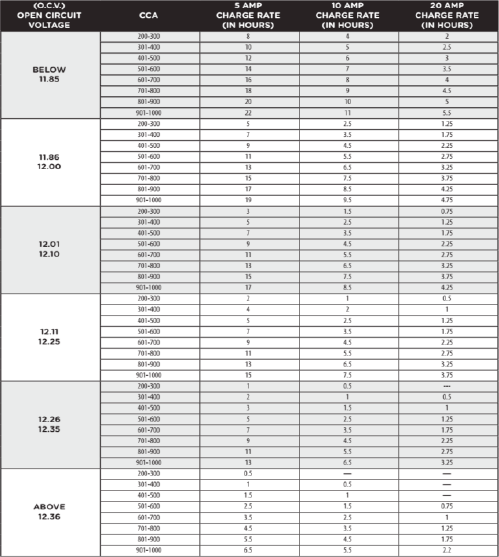
If battery has less than 75% state of charge, it must be recharged before any further testing.
The rate at which battery should be charged depends on:
• Capacity of battery • State of charge
The capacity of battery can be determined one of two ways:
• Reserve Capacity rating (RC) • Cold Cranking Amps rating (CCA)
Once you have determined battery state of charge and battery capacity/rating, use the Exide ™ Technologies Batteries Recharging Chart.

